Microsoft Dataverse is a cloud-based storage space that is used to store and share data. Dataverse is a relatively new name for the Common Data Service, which was previously known as “Windows Azure Storage.”
Dataverse can be accessed through a web browser or through Microsoft’s desktop application. The service provides two different types of storage: one which can be used to store files and another that can only be used to store data sets.
Dataverse has been praised for its easy-to-use interface and its compatibility with Excel, Word, Python, MATLAB, RStudio, SQL Server, and other software.
Microsoft Dataverse is a cloud-based storage space that was previously called the Common Data Service. It was created in order to store and share data. It has been around since 2012, but it is only recently that the name has changed.
Microsoft Dataverse is a cloud-based storage space that is used by a number of organizations. The Dataverse platform is accessed through an application programming interface (API) and provides a centralized data repository, which can be accessed by researchers and data analysts.
Why use Dataverse?
The Microsoft Dynamics 365 and Power Platform applications sit on top of Dataverse and it is used to securely store and manage the data used by these business applications. Like a database, Dataverse has tables, columns, rows, and relationships, but it’s much more than just that. Below are a few of the key benefits:
- Easy to manage – As your data is stored in the cloud you don’t need to worry about the logistics around how it’s stored
- Security – Your data can only be seen by those you grant access to. Additionally, role-based security permissions allow you to control access for different users in your organisation
- Work with any type of data – Dataverse works with any type of relational or non-relational data
- Work with any type of app – Dataverse can work with mobile, web, or desktop apps
- Access your Dynamic 365 data – Your Dynamics 365 data is also stored within Dataverse, enabling you to build apps that use your D365 data and extend it with Power Apps
- Rich Metadata – Use data types and relationships within your Power Apps
- Logic and Processes – Specify columns, business rules, workflows, and processes to strengthen data quality and business processes
- Analytics and Reporting – Dataverse can create charts and reports which can be used with Power BI to create detailed, interactive reports and dashboards
Features and Functionality of Dataverse
Dataverse API
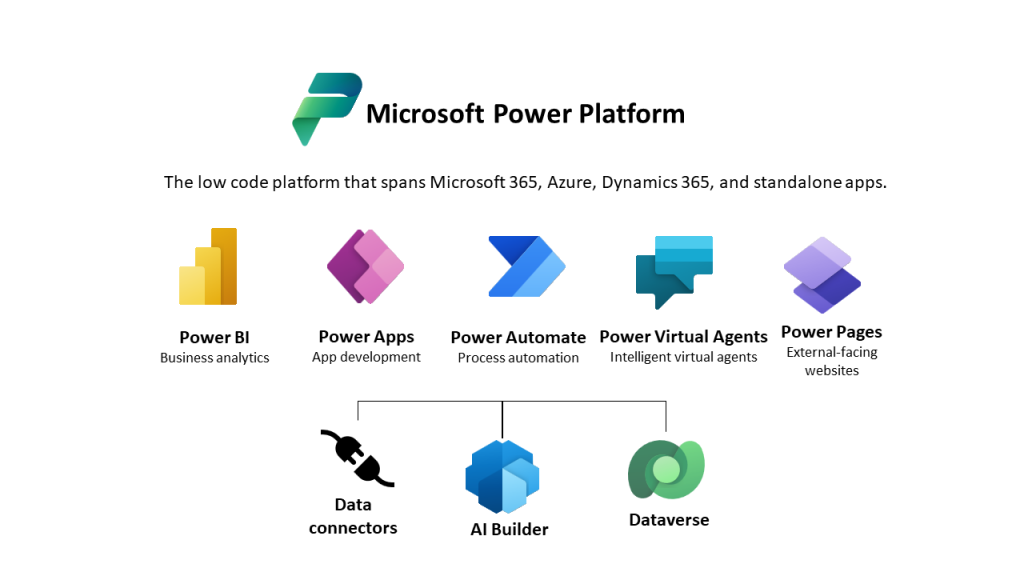
Dataverse has rich API (Application Programming Interface) functionality. This allows your Power Platform applications such as Power Automate, Power Apps, Power BI and Power Virtual Agents to interact with Dataverse directly. Beyond the Power Platform, applications that are in other languages or tools can also interact with Dataverse through a WebAPI.
Model-Driven Power Apps
Model-Driven Power Apps are applications that provide your end-users with a standard set of forms, dashboards and processes. Model-driven apps are built directly into Dataverse which provides you with an easy-to-use interface. This functionality provides the foundation for custom business applications and many of the applications within the Microsoft Dynamics 365 suite.
Dataverse Security
Dataverse has built-in security at the platform level, as opposed to an application level. This means that you can define security roles for a user and these will apply across all applications they are accessing Dataverse from.
Dataverse Logic
Within Dataverse there are lots of ways to configure the logic that makes up an application. There is the data model itself, so the tables and columns and the relationships between them. Calculated and Rollup columns, which can do calculations and aggregations in real-time. An automation engine (Workflows & Power Automate) to build in automation logic and process data. And lots of other components to enhance the user experience, like views, process flows, and business rules. There are also capabilities to develop and implement advanced custom logic on top of the system. This can be done through JavaScript for the user experience, Plug-ins for backend logic & the PowerApps Component Framework for building your own components.
Importing and Exporting Data
Within Dataverse there are lots of ways to configure the logic that makes up an application. There is the data model itself, so the tables and columns and the relationships between them. Calculated and Rollup columns, which can do calculations and aggregations in real-time. An automation engine (Workflows & Power Automate) to build in automation logic and process data. And lots of other components to enhance the user experience, like views, process flows, and business rules. There are also capabilities to develop and implement advanced custom logic on top of the system. This can be done through JavaScript for the user experience, Plug-ins for backend logic & the PowerApps Component Framework for building your own components.
Dataverse and Your Data
Whilst Dataverse provides all of the features and functionality above, it can also be used for just storing data! The structure of Dataverse is based on related tables with a table representing an object, for example a company, person or transaction; these tables are then split into columns such as forename, surname and date of birth. There are different types of tables available within Dataverse, with the most common being standard, custom and activity tables:
– Standard Tables – These can be used in two ways, firstly, as-is if they fit your particular business needs. Or, you can use them as a base for a new table by editing them to meet your specific needs, but you can not delete the standard tables.
– Custom Tables – In order to create a Custom Table you will have to be granted the appropriate security role with Dataverse. You can then edit any Custom Table as well as delete them.
– Activity Tables – Activities refer to notes, emails, appointments, etc
– Virtual Table – These are a type of Custom Table with the difference being that the data used does not come from the Dataverse, instead it comes from another source. The information is also read-only as it is from an external source. Virtual Tables are only owned by organisations.
Dataverse for Teams
Dataverse for Teams is the ‘lite’ version of Dataverse. It is a low-code platform that enables you to build apps using a user-friendly interface whilst remaining in Teams. Essentially, this functionality means your users can create Power Apps, Power Automate flows, and Power Virtual Agents bots without leaving the Teams platform. To find out more about Microsoft Dataverse for Teams, click here.
Get in touch
If you would like to discuss any of the features of Dataverse, Microsoft Dynamics 365 or the Power Platform visit – Seven IT Pro – Power Platform Experts
To book a free consultation for Microsoft power platforms related queries -Book a free consultation Meetings (office365.com)
Leave a Reply